NP Recombinant Protein
Cat# OPCA02215-1MG
Size : 1mg
Brand : Aviva Systems Biology
| Datasheets/Manuals | Printable datasheet for NP Recombinant Protein (Influenza A virus) (OPCA02215) |
|---|
| Predicted Species Reactivity | Influenza A Virus |
|---|---|
| Product Format | Liquid or Lyophilized powder |
| Host | Influenza A virus |
| Additional Information | Relevance: Encapsidates the negative strand viral RNA, protecting it from nucleases. The encapsidated genomic RNA is termed the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) and serves as tplate for transcription and replication. The RNP needs to be localized in the nucleus to start an infectious cycle, but is too large to diffuse through the nuclear pore complex. NP comprises at least 2 nuclear localization signals and is responsible of the active RNP import into the nucleus through the cellular importin alpha/beta pathway. Later in the infection, nucleus export of RNP are mediated through viral proteins NEP interacting with M1 which binds nucleoproteins. It is possible that the nucleoprotein binds directly exportin-1 (XPO1) and plays an active role in RNP nuclear export. M1 interaction with RNP ses to hide nucleoprotein's nuclear localization signals. Soon after a virion infects a new cell, M1 dissociates from the RNP under acidification of the virion driven by M2 protein. Dissociation of M1 from RNP unmask nucleoprotein's nuclear localization signals, targeting the RNP to the nucleus . |
| Reconstitution and Storage | -20°C or -80°C |
| Formulation | 20 mM Tris-HCl based buffer, pH 8.0 |
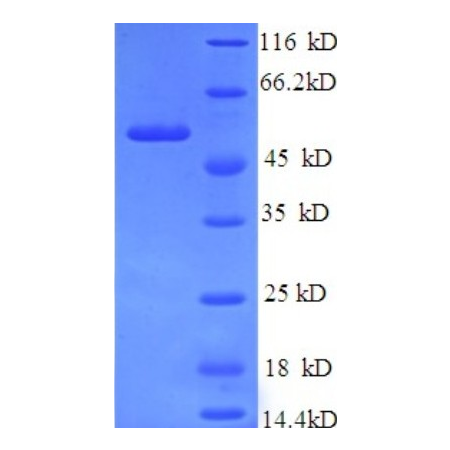
| Purity | Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Peptide Sequence | MASQGTKRSYEQMETDGERQNATEIRASVGKMIDGIGRFYIQMCTELKLSDYEGRLIQNSLTIERMVLSAFDERRNRYLEEHPSAGKDPKKTGGPIYKRVDGRWMRELVLYDKEEIRRIWRQANNGDDATAGLTHMMIWHSNLNDTTYQRTRALVRTGMDPRMCSLMQGSTLPRRSGAAGAAVKGIGTMVMELIRMIKRGINDRNFWRGENGRKTRSAYERMCNILKGKFQTAAQRAMMDQVRESRNPGNAEIEDLIFSARSALILRGSVAHKSCLPACVYGPAVSSGYNFEKEGYSLVGIDPFKLLQNSQVYSLIRPNENPAHKSQLVWMACHSAAFEDLRLLSFIRGTKVSPRGKLSTRGVQIASNENMDNMESSTLELRSRYWAIRTRSGGNTNQQRASAGQISVQPTFSVQRNLPFEKSTVMAAFTGNTEGRTSDMRAEIIRMMEGAKPEEVSFRGRGVFELSDEKATNPIVPSFDMSNEGSYFFGDNAEEYDN |
| Protein Sequence | MASQGTKRSYEQMETDGERQNATEIRASVGKMIDGIGRFYIQMCTELKLSDYEGRLIQNSLTIERMVLSAFDERRNRYLEEHPSAGKDPKKTGGPIYKRVDGRWMRELVLYDKEEIRRIWRQANNGDDATAGLTHMMIWHSNLNDTTYQRTRALVRTGMDPRMCSLMQGSTLPRRSGAAGAAVKGIGTMVMELIRMIKRGINDRNFWRGENGRKTRSAYERMCNILKGKFQTAAQRAMMDQVRESRNPGNAEIEDLIFSARSALILRGSVAHKSCLPACVYGPAVSSGYNFEKEGYSLVGIDPFKLLQNSQVYSLIRPNENPAHKSQLVWMACHSAAFEDLRLLSFIRGTKVSPRGKLSTRGVQIASNENMDNMESSTLELRSRYWAIRTRSGGNTNQQRASAGQISVQPTFSVQRNLPFEKSTVMAAFTGNTEGRTSDMRAEIIRMMEGAKPEEVSFRGRGVFELSDEKATNPIVPSFDMSNEGSYFFGDNAEEYDN |
| Storage Buffer | If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0. |
| Source | E.coli |
| Protein Range | 1-498 aa |
| Tag | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| Reference | Phylogenetic analysis of the entire genome of influenza A (H3N2) viruses from Japan evidence for genetic reassortment of the six internal genes.Lindstrom S.E., Hiromoto Y., Nerome R., Omoe K., Sugita S., Yamazaki Y., Takahashi T., Nerome K.J. Virol. 72:8021-8031(1998) |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | NP |
| Alias Symbols | Nucleocapsid protein. |
| Protein Name | Nucleoprotein |
| Description of Target | Encapsidates the negative strand viral RNA, protecting it from nucleases. The encapsidated genomic RNA is termed the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) and serves as template for transcription and replication. The RNP needs to be localized in the host nucleus to start an infectious cycle, but is too large to diffuse through the nuclear pore complex. NP comprises at least 2 nuclear localization signals that are responsible for the active RNP import into the nucleus through cellular importin alpha/beta pathway. Later in the infection, nclear export of RNPs are mediated through viral proteins NEP interacting with M1 which binds nucleoproteins. It is possible that nucleoprotein binds directly host exportin-1/XPO1 and plays an active role in RNPs nuclear export. M1 interaction with RNP seems to hide nucleoprotein's nuclear localization signals. Soon after a virion infects a new cell, M1 dissociates from the RNP under acidification of the virion driven by M2 protein. Dissociation of M1 from RNP unmasks nucleoprotein's nuclear localization signals, targeting the RNP to the nucleus. |
| Uniprot ID | O91743 |
| Protein Size (# AA) | Full Length |
| Molecular Weight | 60.2 kDa |