Human CD106/VCAM-1 Antibody
Referência OASB00978
Tamanho : 0.1mg
Marca : Aviva Systems Biology
| Datasheets/Manuals | Printable datasheet for Human CD106/VCAM-1 Antibody (OASB00978) |
|---|
| Tested Species Reactivity | Human |
|---|---|
| Predicted Species Reactivity | Human |
| Product Format | Liquid. Supplied as 0.1 mg of purified immunoglobulin in 1.0 mL of borate buffered saline, pH 8.2. No preservatives or amine-containing buffer salts added. |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone | 1.G11B1 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Application | FC, IHC-F, ICC, IP, WB, BL |
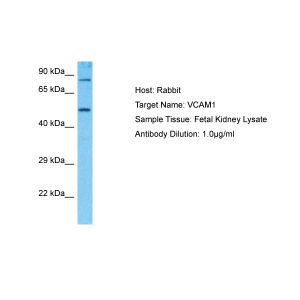
| Additional Information | Description: CD106, also known as INCAM-110, is a 110 kDa vascular adhesion cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) that is member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD106 is expressed predominantly on cytokine-activated vascular endothelium but has also been identified on interfollicular dendritic cells, some macrophages, and bone marrow stromal cells. Endothelial CD106 binds the integrins alpha4/beta1 (CD49d/CD29, VLA-4) and alpha4/beta7 and contributes to extravasation of lymphocytes, monocytes, basophils, and eosinophils (but not neutrophils) from blood vessels, particularly at sites of inflammation. Unlike the beta2 integrins, the CD106-VLA-4 interaction can mediate both the initial tethering and rolling of lymphocytes on endothelium as well as their subsequent arrest and firm adhesion. CD106 expressed on non-vascular tissues has been implicated in the interaction of hematopoietic progenitors with bone marrow stromal cells, B cell binding to follicular dendritic cells, costimulation of T cells, and embryonic development. The monoclonal antibody 1.G11B1 inhibits in vitro binding of lymphocytes and monocytes to VCAM-1 on stimulated endothelium. |
| Reconstitution and Storage | Store at 2-8C |
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL |
| Specificity | CD106 |
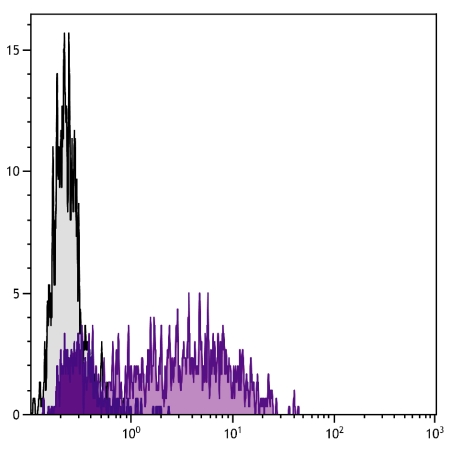
| Characterization | To insure lot to lot consistency, each batch of product is tested by flow cytometry to conform with thecharacteristics of a standard reference reagent. |
| Application Info | Flow cytometry: <=1 ug/10^6 cells |
| Other Applications Data | Since applications vary, you should determine the optimum workingdilution of the product that is appropriate for your specific need. |
| Reference | 1. Schlossman, S., L. Bloumsell, W. Gilks, J.M. Harlan, C. Kishimoto, J. Ritz, S. Shaw, R. Silverstein, T. Springer, T.F. Tedder, and R.F. Todd,eds. 1995. Leukocyte Typing V: White Cell Differentiation Antigens, Oxford University Press, Oxford 2. Barclay, A.N., M.H. Brown, S.K.A. Law, A.J. McKnight, M.G. Tomlinson, and P.A. van der Merwe, eds. 1997. The Leukocyte AntigensFacts Book, 2nd Edition, CD106Section, Academic Press, New York, p. 386 3. Thornhill, M.H., S.M. Wellicome, D.L. Mahiouz, J.S. Lanchbury, U. Kyan- Aung, and D.O. Haskard. 1991. J. Immunol. 146:592 4. Bevilacqua, M.P. 1993. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 11:767. |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | VCAM1 |
| Gene Full Name | Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 |
| Alias Symbols | CD106, INCAM-100 |
| NCBI Gene Id | 7412; 396925 |
| Protein Name | vascular cell adhesion protein 1 |
| Description of Target | This gene is a member of the Ig superfamily and encodes a cell surface sialoglycoprotein expressed by cytokine-activated endothelium. This type I membrane protein mediates leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and signal transduction, and may play a role in the development of artherosclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Three alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. |
| Uniprot ID | P19320, Q28939 |
| Protein Accession # | NP_001069.1 |
| Nucleotide Accession # | NM_001078.3 |
| Molecular Weight | 110 kDa |